Primary
and Secondary Nutrients
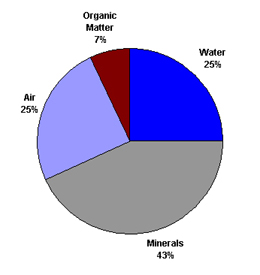
Nutrients
are critical to healthy plants, but we should not forget that,
without sunlight, air, and water, nothing can survive. Healthy,
rich, un-compacted soil is made up of components in the percentages
shown in the accompanying graph. |
Nitrogen
(N)
-
Nitrogen
is a part of all living cells and is a necessary part of all proteins,
enzymes and metabolic processes involved in the synthesis and transfer
of energy.
-
Nitrogen
is a part of chlorophyll, the green pigment of the plant that is
responsible for photosynthesis.
-
Helps
plants with rapid growth, increasing seed and fruit production and
improving the quality of leaf and forage crops.
-
Nitrogen
often comes from fertilizer application and from the air (legumes
get their N from the atmosphere, water or rainfall contributes very
little nitrogen)
|
 |
Phosphorus
(P)
-
Like nitrogen, phosphorus (P) is an essential part of the process
of photosynthesis.
-
Involved
in the formation of all oils, sugars, starches, etc.
-
Helps with the transformation of solar energy into chemical energy;
proper plant maturation; withstanding stress.
-
Effects rapid growth.
-
Encourages blooming and root growth.
-
Phosphorus often comes from fertilizer, bone meal, and superphosphate.
Potassium
(K)
-
Potassium is absorbed by plants in larger amounts than any other
mineral element except nitrogen and, in some cases, calcium.
-
Helps
in the building of protein, photosynthesis, fruit quality and reduction
of diseases.
-
Potassium is supplied to plants by soil minerals, organic materials,
and fertilizer
Calcium
(Ca)
-
Calcium,
an essential part of plant cell wall structure, provides for normal
transport and retention of other elements as well as strength in
the plant. It is also thought to counteract the effect of alkali
salts and organic acids within a plant.
-
Sources
of calcium are dolomitic lime, gypsum, and superphosphate.
Magnesium
(Mg)
-
Magnesium is part of the chlorophyll in all green plants and essential
for photosynthesis. It also helps activate many plant enzymes needed
for growth.
-
Soil minerals, organic material, fertilizers, and dolomitic limestone
are sources of magnesium for plants.
Sulfur
(S)
-
Essential plant food for production of protein.
-
Promotes activity and development of enzymes and vitamins.
-
Helps in chlorophyll formation.
-
Improves root growth and seed production.
-
Helps with vigorous plant growth and resistance to cold.
-
Sulfur may be supplied to the soil from rainwater. It is also added
in some fertilizers as an impurity, especially the lower grade fertilizers.
The use of gypsum also increases soil sulfur levels.
Courtesy: Agricultural
Department, University of North Carolina. |
|